壳聚糖是由D-葡萄糖胺和N-乙酰基-D-葡萄糖胺组成的线性多糖,其中D-葡萄糖胺和N-乙酰基-D-葡萄糖胺之间通过β-1,4糖苷键连接(图1)[1]。提取壳聚糖的原料来源广泛,资源丰富,主要包括虾蟹壳、植物、微生物和昆虫[2-4]。壳聚糖具有良好的生物相容性、无毒性及较好的成膜性等特点,还能够有效抑制肉与肉制品氧化及微生物腐败[5],在肉类产业中得以广泛应用[6-8]。
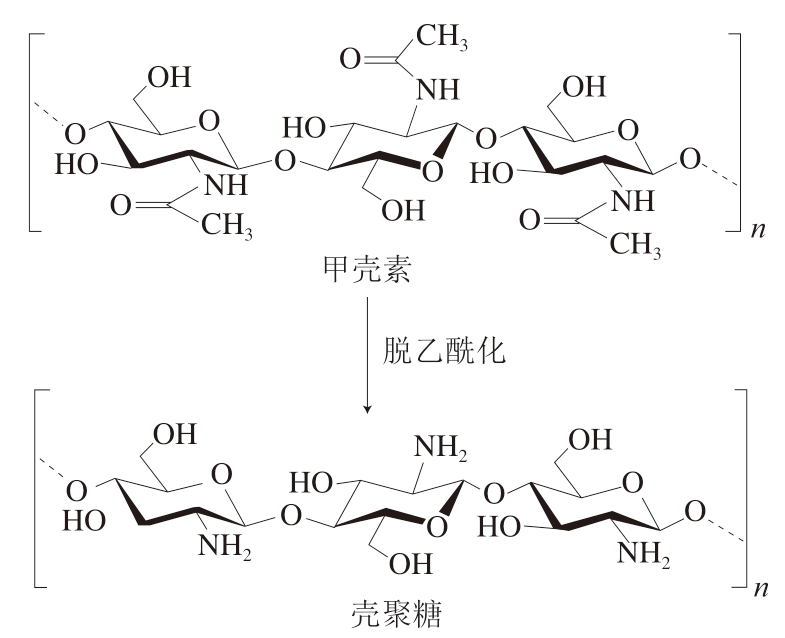
图1 壳聚糖结构[9]
Fig.1 Structure of chitosan[9]
然而,壳聚糖在肉与肉制品保鲜中的确切抑菌机制仍需进一步明确。同时,虽然目前已有诸多关于壳聚糖在肉与肉制品保鲜中应用的研究,但仍缺乏对壳聚糖在肉与肉制品保鲜中的应用方式、应用效果、影响因素及与其他技术协同作用的系统总结。因此,本文综述壳聚糖在肉类产业中的应用研究进展,壳聚糖在肉与肉制品中的保鲜机制、影响因素及能与壳聚糖起协同作用的相关技术。
1 壳聚糖在肉与肉制品中的应用方式及影响因素
1.1 壳聚糖在肉与肉制品中的应用方式
壳聚糖的作用效果受使用方式和添加量影响,为了使壳聚糖在肉与肉制品中发挥最大作用,应选择合适的使用方式和添加量。近年来,壳聚糖主要通过以下2 种方式应用于肉与肉制品保鲜:1)制备壳聚糖复合薄膜;2)制备壳聚糖复合涂层。
壳聚糖复合涂层和壳聚糖复合薄膜水蒸气渗透率低、机械强度差,在肉与肉制品保鲜中的应用受到限制,因而通常将壳聚糖与其他物质复合,制成壳聚糖复合薄膜或复合涂层来改善壳聚糖在肉与肉制品中的应用性能[9]。壳聚糖复合薄膜的制备方式主要有2 种:溶液流延法和层层挤出法[10]。由于溶液流延法操作简单而被广泛应用,其主要包括以下6 个步骤:1)使用酸性溶液(一般为醋酸溶液)溶解壳聚糖;2)根据不同的体积比或质量比与其他物质混合;3)搅拌获得均匀、黏稠溶液;4)通过过滤、离心和超声等方式除去溶液中残留的气泡和不溶性颗粒;5)将溶液均匀平铺于干燥、洁净的平板;6)干燥冷却后将薄膜剥离平板[11-12]。Siripatrawan等[13]将绿茶提取物与壳聚糖混合制成绿茶提取物-壳聚糖混合薄膜,结果表明,绿茶提取物的加入可有效改善壳聚糖薄膜的拉伸强度和断裂伸长率等机械性能。此外,将果胶与壳聚糖混合制成果胶-壳聚糖复合薄膜可有效改善壳聚糖薄膜的透明度和机械性能等[10]。含有葵花籽油的壳聚糖薄膜能够有效减缓猪肉汉堡高铁肌红蛋白含量的增加,同时抑制汉堡中微生物的生长[14]。将均匀、黏稠的壳聚糖复合溶液直接涂在肉类等食品表面可以形成壳聚糖复合涂层[15-17]。Zheng Kaixi等[18]研究表明,含有牛至精油的壳聚糖涂层能够显著抑制冷藏鸡胸肉中微生物的生长,同时抑制其脂质氧化和蛋白质氧化。
1.2 壳聚糖在肉制品中应用的影响因素
壳聚糖的应用效果受到很多因素的影响,肉与肉制品表面微生物的类型和细胞生长阶段会影响壳聚糖的应用效果,壳聚糖的脱乙酰度、分子质量及浓度等也均会对壳聚糖的应用效果产生显著影响[19]。
1.2.1 壳聚糖的分子质量
壳聚糖分为低分子质量(<100 kDa)、中分子质量(100~1 000 kDa)和高分子质量(>1 000 kDa)3 种类型[20]。研究表明,低分子质量壳聚糖更有利于保持肉与肉制品的品质。Li Xiaofang等[21]对比研究3、50、1 000 kDa壳聚糖溶液的抑菌活性,结果表明,50 kDa壳聚糖溶液对大肠杆菌的抑制作用最强。Ye Mu等[22]研究发现,低分子质量壳聚糖对于单核细胞增生李斯特氏菌的抑制作用比中分子质量的壳聚糖更强。
1.2.2 壳聚糖的脱乙酰度
壳聚糖可分为低(55%~70%)、中(70%~85%)、高(85%~95%)、超高(95%以上)脱乙酰度4 种类型[23]。在肉与肉制品贮藏保鲜中,所使用壳聚糖的脱乙酰度一般在90%以上,为高脱乙酰度壳聚糖。脱乙酰度高的壳聚糖对微生物的抑制作用较强,原因为壳聚糖脱乙酰度越高,所携带的正电荷越多[24],溶解度越大,结晶越少,反应活性越强[25](表1)。
表1 不同壳聚糖溶液对应用效果的影响
Table 1 Antimicrobial effect of different chitosan solutions
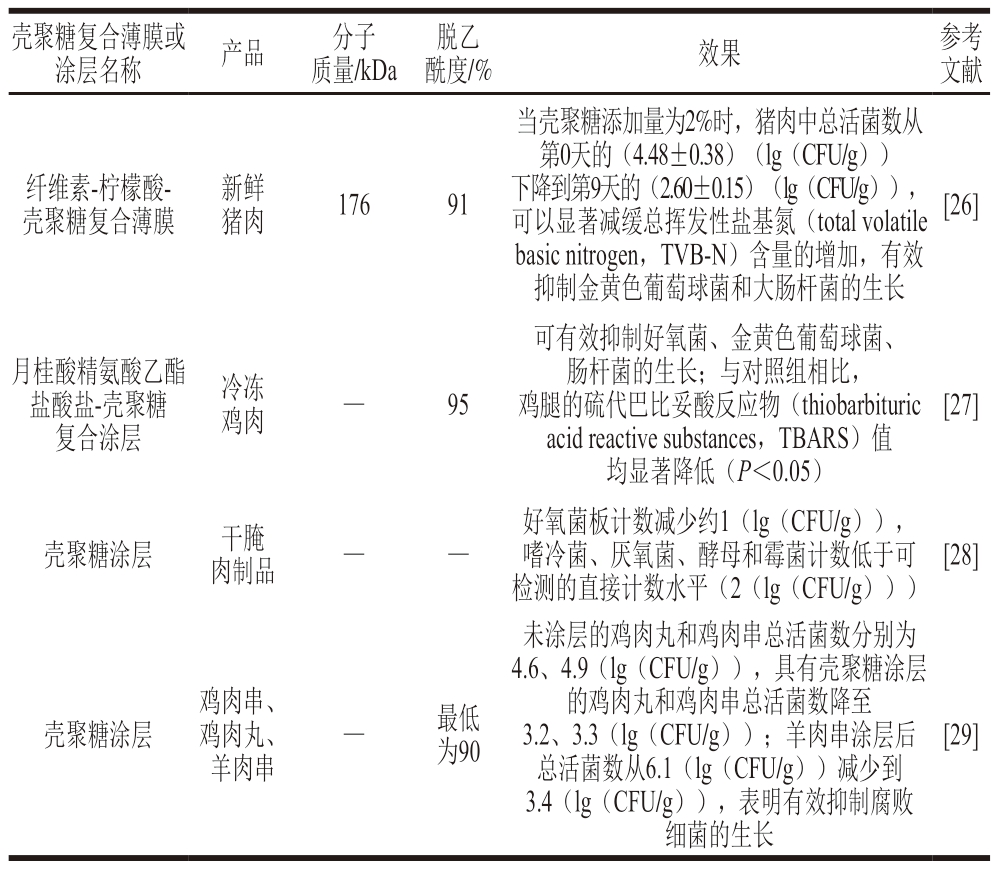
注:—.文献未提及。
壳聚糖复合薄膜或涂层名称产品分子质量/kDa 酰度/%效果参考文献脱乙纤维素-柠檬酸-壳聚糖复合薄膜新鲜猪肉17691当壳聚糖添加量为2%时,猪肉中总活菌数从第0天的(4.48±0.38)(lg(CFU/g))下降到第9天的(2.60±0.15)(lg(CFU/g)),可以显著减缓总挥发性盐基氮(total volatile basic nitrogen,TVB-N)含量的增加,有效抑制金黄色葡萄球菌和大肠杆菌的生长[26]月桂酸精氨酸乙酯盐酸盐-壳聚糖复合涂层冷冻鸡肉—95可有效抑制好氧菌、金黄色葡萄球菌、肠杆菌的生长;与对照组相比,鸡腿的硫代巴比妥酸反应物(thiobarbituric acid reactive substances,TBARS)值均显著降低(P<0.05)[27]壳聚糖涂层干腌肉制品——好氧菌板计数减少约1(lg(CFU/g)),嗜冷菌、厌氧菌、酵母和霉菌计数低于可检测的直接计数水平(2(lg(CFU/g)))[28]壳聚糖涂层鸡肉串、鸡肉丸、羊肉串—最低为90未涂层的鸡肉丸和鸡肉串总活菌数分别为4.6、4.9(lg(CFU/g)),具有壳聚糖涂层的鸡肉丸和鸡肉串总活菌数降至3.2、3.3(lg(CFU/g));羊肉串涂层后总活菌数从6.1(lg(CFU/g))减少到3.4(lg(CFU/g)),表明有效抑制腐败细菌的生长[29]
2 壳聚糖在肉与肉制品应用中的保鲜机制
2.1 壳聚糖的抗菌活性
微生物的腐败作用是导致肉与肉制品腐败变质的主要因素。导致肉与肉制品腐败的微生物种类繁多,主要包括假单胞菌属、肠杆菌、乳酸菌、梭状芽孢杆菌、不动杆菌、热杀环丝菌和希瓦氏菌等[30]。腐败微生物分解肉类产品中的脂肪、碳水化合物和蛋白质,导致异味、变色和形成黏液,从而使其丧失可食用性[31]。壳聚糖主要通过4 个途径产生抗菌活性:1)静电作用。由于壳聚糖的氨基可以质子化,从而使壳聚糖带正电荷。当pH值低于pKa值时,壳聚糖的—NH2基团转化为质子化形式—NH3+。革兰氏阳性菌的细胞壁含有含磷壁酸的厚肽聚糖层,使得细胞表面带有负电荷;革兰氏阴性菌的细胞壁含有脂多糖,使得细胞表面的负电荷较多,从而使其对壳聚糖更加敏感。壳聚糖与微生物之间发生静电作用,破坏细胞完整性,引起细胞内容物泄漏,造成酶和核苷酸等成分损失,导致微生物死亡[32-33]。Hao Peiyan等[34]研究表明,姜黄环糊精接枝壳聚糖水凝胶可通过—NH3+与细菌表面负电荷的静电作用抑制微生物的生长,姜黄环糊精接枝壳聚糖水凝胶对金黄色葡萄球菌的抑制作用强于大肠杆菌。壳聚糖也可抑制真菌的生长,对壳聚糖敏感的真菌细胞膜比壳聚糖抗性真菌含有更多的多不饱和脂肪酸,这表明壳聚糖的抑菌效果可能与细胞膜的流动性密切相关[35]。2)与微生物DNA的相互作用。低分子质量的壳聚糖可以进入微生物的细胞核,通过与微生物DNA分子相互作用抑制微生物增殖[36];Xing Ke等[37]研究油酰基-壳聚糖纳米颗粒对核酸电泳迁移率的影响,当油酰基-壳聚糖纳米颗粒质量浓度达到1 000 mg/L时,大肠杆菌DNA和RNA的迁移被完全抑制。3)抑制微生物细胞内的代谢酶。利用壳聚糖的螯合作用阻断微生物的活性中心,从而抑制其生长[38]。4)阻隔作用。高分子质量的壳聚糖涂层或薄膜会在肉与肉制品表面形成阻隔层,减少氧气的传递和营养物质的吸收,同时阻止代谢产物的排泄,从而抑制微生物的代谢活动[19]。壳聚糖的抑菌机制如图2所示。
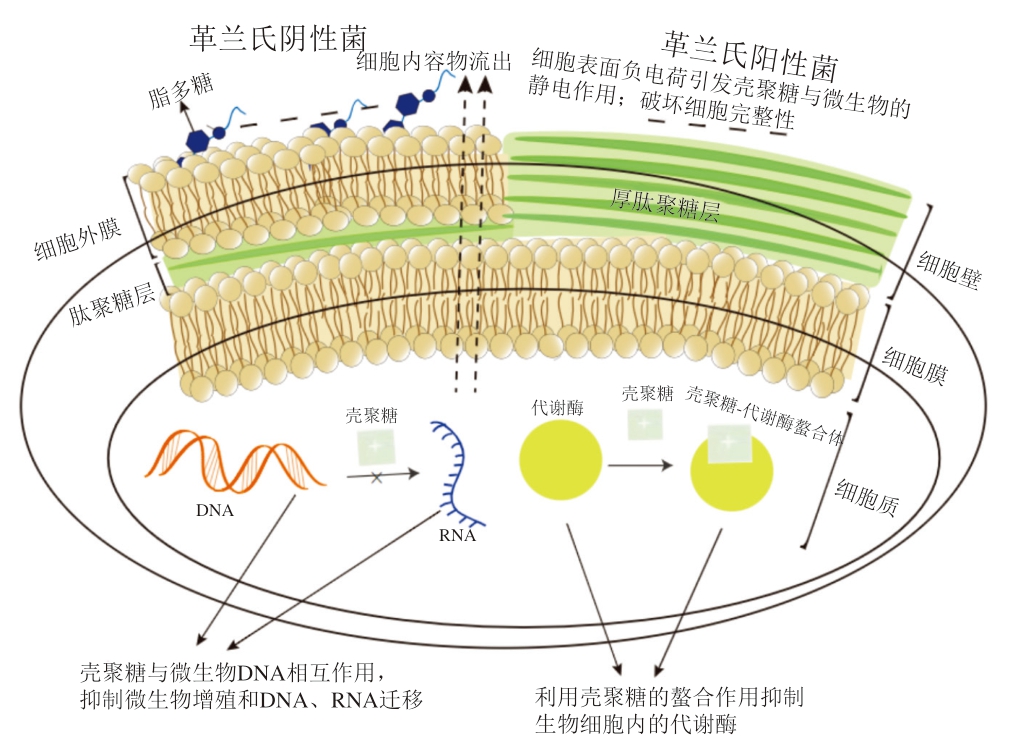
图2 壳聚糖的抑菌机制
Fig.2 Antimicrobial mechanism of chitosan
2.2 壳聚糖的抗氧化活性
在肉类加工过程中,脂质氧化和蛋白氧化是引起其品质劣变的主要非微生物因素[39-40]。脂质氧化和蛋白质氧化可导致肉与肉制品营养成分显著减少和颜色劣变[41-42]。壳聚糖的抗氧化活性主要归因于其氨基清除自由基的能力,研究发现,壳聚糖不但可以显著减少蛋白质氧化[43],还可以通过螯合作用延缓食品中的脂质氧化[44]。除此之外,壳聚糖薄膜可以阻碍肉品与氧气接触,减少氧气的转移,从而使氧化作用减弱[45]。需要指出的是,壳聚糖虽然具有一定的抗氧化活性,但是单独使用的壳聚糖薄膜或壳聚糖涂层的抗氧化活性较低,应用效果较差,因此通常将壳聚糖与其他物质混合制成壳聚糖复合薄膜或复合涂层来提高其抗氧化活性[46]。
3 强化壳聚糖在肉与肉制品中应用效果的技术
壳聚糖涂层机械强度差,水蒸气渗透性低,限制了其在肉与肉制品中的应用。因此,其通常与其他保鲜技术相结合,从而保证肉的品质并延长货架期[47]。
3.1 与植物精油结合
精油是从植物中提取的挥发性芳香油状液体,具有抗菌、抗氧化等多种生物活性;但植物精油有强烈的风味,可能改变肉制品的感官品质。此外,植物精油不稳定,在受热、光照条件下容易氧化分解[48]。壳聚糖具有一定的控释能力和黏附性,有利于天然抗菌剂的靶向释放,延长天然抗菌剂发挥活性的时间。例如,壳聚糖纳米乳液可以将天然抗菌剂包埋在其内部,增强天然抗菌剂的抑菌活性和稳定性[49],同时可以起到屏障作用,阻止水分流失和氧气迁移,从而维持肉制品品质[50]。因此,利用植物精油和壳聚糖的协同作用来抑制肉类产品品质劣变受到国内外学者的广泛关注(表2)。
表2 植物精油和壳聚糖协同使用在肉制品保鲜中的应用
Table 2 Application of plant essential oil combined with chitosan in the preservation of meat products

精油种类应用产品应用效果参考文献茴香精油和肉桂醛猪肉饼有效抑制猪肉饼中大肠杆菌和金黄色葡萄球菌,将猪肉饼的货架期从6 d延长至10 d[51]百里香精油冷藏猪肉抑制腐败微生物的生长,同时可以保护肉色和抑制异味产生,从而延长肉类产品货架期[52]柑橘精油新鲜猪肉有效抑制猪肉中大肠杆菌和金黄色葡萄球菌的生长[53]肉桂精油和迷迭香提取物鸡肉饼纳米乳液处理样品的TBARS值、pH值、TVB-N含量和总活菌数最低,纳米乳液涂层极大减少鸡肉饼水分流失,将其保质期延长4 d以上[54]
3.2 与物理方法相结合
物理方法是肉与肉制品保鲜的常用手段。传统的热灭菌是指在不低于121 ℃的湿热条件下灭活包括孢子在内的腐败微生物,从而延长食品的保质期,但是传统热灭菌方式严重损害了食品质量和感官品质[55]。近年来,超高压、等离子体技术和紫外线辐射等非热灭菌技术受到国内外食品科学家的共同关注[56]。将壳聚糖与物理方法相结合可有效提高肉与肉制品的感官品质,延长其货架期(表3)。
表3 壳聚糖涂层与物理方法相结合在肉制品保鲜中的应用
Table 3 Application of chitosan coating combined with physical methods in the preservation of meat products

物理方法应用产品应用效果参考文献γ辐照冷藏鸡肉含有葡萄籽提取物(2.0%)的壳聚糖涂层(1%)结合γ辐照可显著降低TBARS值,抑制腐败微生物生长,将冷藏鸡肉的货架期延长至贮藏结束(21 d)[57]热处理红烧鸭肉壳聚糖涂层结合热处理能够抑制微生物的多样性,对肠杆菌的抑制作用尤为明显,并且能够降低羰基含量,从而改善红烧鸭肉的品质并延长其货架期[6]高氧气调包装新鲜猪肉在2 ℃条件下,高氧气调包装结合含有没食子酸的壳聚糖能够有效抑制蛋白质氧化和脂质氧化[58]
3.3 与其他活性物质复合
迄今为止,GB 2760—2014《食品安全国家标准 食品添加剂》已批准壳聚糖、明胶、海藻酸钠等物质可直接添加在肉类制品中。将壳聚糖与这些物质相结合不仅可以提高壳聚糖涂层的机械性能,而且可以有效抑制肉与肉制品中腐败微生物的生长(表4)。
表4 壳聚糖与其他物质相结合在肉制品保鲜中的应用
Table 4 Application of chitosan combined with other substances in the preservation of meat products
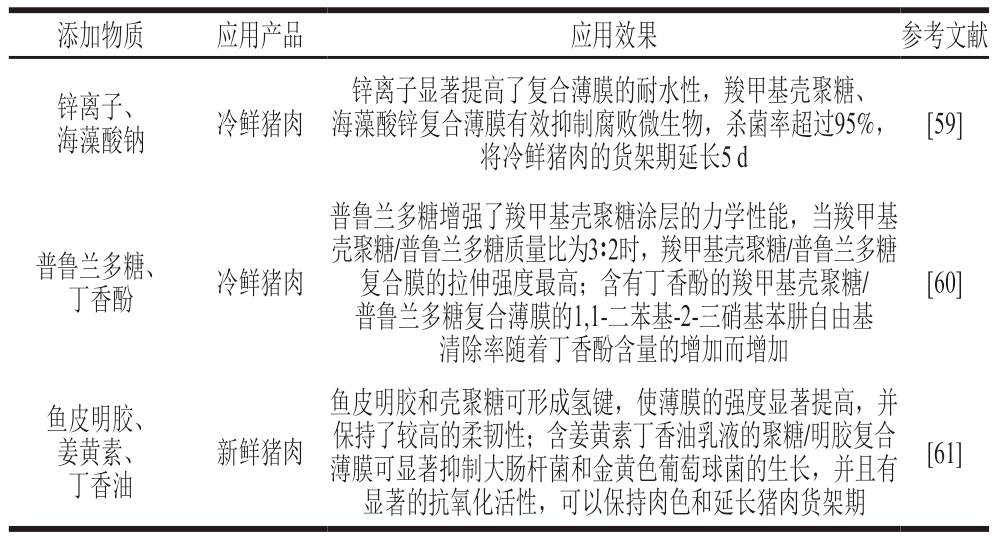
添加物质应用产品应用效果参考文献锌离子、海藻酸钠冷鲜猪肉锌离子显著提高了复合薄膜的耐水性,羧甲基壳聚糖、海藻酸锌复合薄膜有效抑制腐败微生物,杀菌率超过95%,将冷鲜猪肉的货架期延长5 d[59]普鲁兰多糖、丁香酚冷鲜猪肉普鲁兰多糖增强了羧甲基壳聚糖涂层的力学性能,当羧甲基壳聚糖/普鲁兰多糖质量比为3∶2时,羧甲基壳聚糖/普鲁兰多糖复合膜的拉伸强度最高;含有丁香酚的羧甲基壳聚糖/普鲁兰多糖复合薄膜的1,1-二苯基-2-三硝基苯肼自由基清除率随着丁香酚含量的增加而增加[60]鱼皮明胶、姜黄素、丁香油新鲜猪肉鱼皮明胶和壳聚糖可形成氢键,使薄膜的强度显著提高,并保持了较高的柔韧性;含姜黄素丁香油乳液的聚糖/明胶复合薄膜可显著抑制大肠杆菌和金黄色葡萄球菌的生长,并且有显著的抗氧化活性,可以保持肉色和延长猪肉货架期[61]
4 结 语
肉与肉制品营养丰富,在贮藏、加工、运输和销售等过程中极易发生腐败变质。因此,新型肉类保鲜技术的研发对于肉类产业的发展至关重要。壳聚糖作为一种生物大分子,具有良好的安全性和成膜性,并且满足了消费者希望使用天然无毒物质代替化学物质的需求,在肉与肉制品的保鲜中有巨大的应用潜力。
壳聚糖可以通过制备壳聚糖复合薄膜和壳聚糖复合涂层2 种方式来提高肉与肉制品的品质并延长货架期。其可以通过静电作用影响微生物细胞膜、抑制DNA转录、抑制微生物细胞内的代谢酶及改变细胞膜的通透性,从而抑制微生物增殖。壳聚糖的分子质量越小、脱乙酰度越高,其在肉制品中的抑菌活性越高,可通过与植物精油相结合、与物理灭菌方法相结合、与其他活性物质复合使用等方式强化壳聚糖在肉与肉制品中的应用效果。
然而,壳聚糖在肉与肉制品保鲜中的应用仍然存在一些问题,壳聚糖自身的抗菌活性和抗氧化活性较低,需要与其他物质协同作用才能产生更好的保鲜效果,但添加物质可能会影响肉与肉制品的风味;添加物质在壳聚糖涂层中分布不均也可能降低保鲜效果等。总的来说,壳聚糖在肉与肉制品的保鲜中有较好的应用前景,随着上述问题的不断解决,壳聚糖在肉与肉制品保鲜中的应用将会更加广泛。
[1] HARUGADE A, SHERJE A P, PETHE A.Chitosan: a review on properties, biological activities and recent progress in biomedical applications[J].Reactive and Functional Polymers, 2023, 191: 105634.DOI:10.1016/j.reactfunctpolym.2023.105634.
[2] NEGM N A, HEFNI H H H, ABD-ELAAL A A A, et al.Advancement on modification of chitosan biopolymer and its potential applications[J].International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2020, 152: 681-702.DOI:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.02.196.
[3] RAHIMI M, MIR S M, BAGHBAN R, et al.Chitosan-based biomaterials for the treatment of bone disorders[J].International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2022, 215: 346-367.DOI:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2022.06.079.
[4] 封晴霞, 赵雄伟, 陈志周, 等.壳聚糖及其应用研究进展[J].食品工业科技, 2018, 39(21): 333-336; 341.DOI:10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2018.21.058.
[5] MONDÉJAR-LÓPEZ M, CASTILLO R, JIMÉNEZ A J L, et al.Polysaccharide film containing cinnamaldehyde-chitosan nanoparticles, a new eco-packaging material effective in meat preservation[J].Food Chemistry, 2023, 4371(1): 137710.DOI:10.1016/j.foodchem.2023.137710.
[6] LI H H, QU S J, MA P, et al.Effects of chitosan coating combined with thermal treatment on physicochemical properties, bacterial diversity and volatile flavor of braised duck meat during refrigerated storage[J].Food Research International, 2023, 167: 112627.DOI:10.1016/j.foodres.2023.112627.
[7] PARICHANON P, ASCRIZZI R, TANI C, et al.The protective combined effect of chitosan and essential oil coatings on cheese and cured meat against the oviposition of Piophila casei[J].Food Bioscience, 2023, 56: 103132.DOI:10.1016/j.fbio.2023.103132.
[8] ZHAO Q L, FAN L P, LIU Y F, et al.Recent advances on formation mechanism and functionality of chitosan-based conjugates and their application in o/w emulsion systems: a review[J].Food Chemistry,2022, 380: 131838.DOI:10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.131838.
[9] AFROZ ALI S M, NIAZ T, MUNIR A, et al.Potential of pectinchitosan based composite films embedded with quercetin-loaded nanofillers to control meat associated spoilage bacteria[J].Food Bioscience, 2023, 53: 102547.DOI:10.1016/j.fbio.2023.102547.
[10] KUMAR S, MUKHERJEE A, DUTTA J.Chitosan based nanocomposite films and coatings: emerging antimicrobial food packaging alternatives[J].Trends in Food Science and Technology,2020, 97: 196-209.DOI:10.1016/j.tifs.2020.01.002.
[11] MATHEW S, BRAHMAKUMAR M, ABRAHAM T E.Microstructural imaging and characterization of the mechanical,chemical, thermal, and swelling properties of starch-chitosan blend films[J].Biopolymers, 2006, 82(2): 176-187.DOI:10.1002/bip.20480.
[12] YUAN D D, HAO X, LIU G R, et al.A novel composite edible film fabricated by incorporating W/O/W emulsion into a chitosan film to improve the protection of fresh fish meat[J].Food Chemistry, 2022,385: 132647.DOI:10.1016/j.foodchem.2022.132647.
[13] SIRIPATRAWAN U, HARTE B R.Physical properties and antioxidant activity of an active film from chitosan incorporated with green tea extract[J].Food Hydrocolloids, 2010, 24(8): 770-775.DOI:10.1016/j.foodhyd.2010.04.003.
[14] VARGAS M, ALBORS A, CHIRALT A.Application of chitosansunflower oil edible films to pork meat hamburgers[J].Procedia Food Science, 2011, 1: 39-43.DOI:10.1016/j.profoo.2011.09.007.
[15] VASILATOS G C, SAVVAIDIS I N.Chitosan or rosemary oil treatments, singly or combined to increase turkey meat shelf-life[J].International Journal of Food Microbiology, 2013, 166(1): 54-58.DOI:10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2013.06.018.
[16] CAO Y J, SONG Z Y, DONG C J, et al.Chitosan coating with grape peel extract: a promising coating to enhance the freeze-thaw stability of beef[J].Meat Science, 2023, 204: 109262.DOI:10.1016/j.meatsci.2023.109262.
[17] JIN J, LUO B D, XUAN S M, et al.Degradable chitosan-based bioplastic packaging: design, preparation and applications[J].International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2024, 266(1):131253.DOI:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.131253.
[18] ZHENG K X, LI B, LIU Y, et al.Effect of chitosan coating incorporated with oregano essential oil on microbial inactivation and quality properties of refrigerated chicken breasts[J].LWTFood Science and Technology, 2023, 176: 114547.DOI:10.1016/j.lwt.2023.114547.
[19] HOSSEINNEJAD M, JAFARI S M.Evaluation of different factors affecting antimicrobial properties of chitosan[J].International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2016, 85: 467-475.DOI:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2016.01.022.
[20] GONCALVES C, FERREIRA N, LOURENCO L.Production of low molecular weight chitosan and chitooligosaccharides(COS): a review[J].Polymers, 2021, 13(15): 2466.DOI:10.3390/polym13152466.
[21] LI X F, FENG X Q, YANG S, et al.Chitosan kills Escherichia coli through damage to be of cell membrane mechanism[J].Carbohydrate Polymers, 2010, 79(3): 493-499.DOI:10.1016/j.carbpol.2009.07.011.
[22] YE M, NEETOO H, CHEN H Q.Control of Listeria monocytogenes on ham steaks by antimicrobials incorporated into chitosancoated plastic films[J].Food Microbiology, 2008, 25(2): 260-268.DOI:10.1016/j.fm.2007.10.014.
[23] LÜ S H.High-performance superplasticizer based on chitosan[M]//PACHECO-TORGAL F, IVANOV V, KARAK N, et al.Biopolymers and biotech admixtures for eco-efficient construction materials.Sawston Cambridge: Woodhead Publishing, 2016: 131-150.DOI:10.1016/b978-0-08-100214-8.00007-5.
[24] TOLAIMATE A, DESBRIERES J, RHAZI M, et al.Contribution to the preparation of chitins and chitosans with controlled physicochemical properties[J].Polymer, 2003, 44(26): 7939-7952.DOI:10.1016/j.polymer.2003.10.025.
[25] BYUN S M, NO H K, HONG J H, et al.Comparison of physicochemical, binding, antioxidant and antibacterial properties of chitosans prepared from ground and entire crab leg shells[J].International Journal of Food Science and Technology, 2013, 48(1):136-142.DOI:10.1111/j.1365-2621.2012.03169.x.
[26] SONG Z Y, MA T C, ZHI X J, et al.Cellulosic films reinforced by chitosan-citric complex for meat preservation: influence of nonenzymatic browning[J].Carbohydrate Polymers, 2021, 272:118476.DOI:10.1016/j.carbpol.2021.118476.
[27] ABDEL-NAEEM H H S, ZAYED N E R, MANSOUR H A.Effect of chitosan and lauric arginate edible coating on bacteriological quality,deterioration criteria, and sensory attributes of frozen stored chicken meat[J].LWT-Food Science and Technology, 2021, 150: 111928.DOI:10.1016/j.lwt.2021.111928.
[28] ABDALLAH M R S, MOHAMED M A, MOHAMED H M H, et al.Improving the sensory, physicochemical and microbiological quality of pastirma (a traditional dry cured meat product) using chitosan coating[J].LWT-Food Science and Technology, 2017, 86: 247-253.DOI:10.1016/j.lwt.2017.08.006.
[29] KANATT S R, RAO M S, CHAWLA S P, et al.Effects of chitosan coating on shelf-life of ready-to-cook meat products during chilled storage[J].LWT-Food Science and Technology, 2013, 53(1): 321-326.DOI:10.1016/j.lwt.2013.01.019.
[30] PENNACCHIA C, ERCOLINI D, VILLANI F.Spoilage-related microbiota associated with chilled beef stored in air or vacuum pack[J].Food Microbiology, 2011, 28(1): 84-93.DOI:10.1016/j.fm.2010.08.010.
[31] PELLISSERY A J, VINAYAMOHAN P G, AMALARADJOU M A R, et al.Spoilage bacteria and meat quality[M]//BISWAS A K, MANDAL P K.Meat quality analysis.Salt Lake City: Academic Press, 2020: 307-334.DOI:10.1016/B978-0-12-819233-7.00017-3.
[32] YU J T, WANG D P, GEETHA N, et al.Current trends and challenges in the synthesis and applications of chitosan-based nanocomposites for plants: a review[J].Carbohydrate Polymers, 2021, 261: 117904.DOI:10.1016/j.carbpol.2021.117904.
[33] WANG Q Z, CHEN X G, LIU N, et al.Protonation constants of chitosan with different molecular weight and degree of deacetylation[J].Carbohydrate Polymers, 2006, 65(2): 194-201.DOI:10.1016/j.carbpol.2006.01.001.
[34] HAO P Y, ZHOU H Y, REN L J, et al.Preparation and antibacterial properties of curcumin-loaded cyclodextrin-grafted chitosan hydrogel[J].Journal of Sol-Gel Science and Technology, 2023, 106(3):877-894.DOI:10.1007/s10971-023-06097-8.
[35] MATICA M A, AACHMANN F L, TONDERVIK A, et al.Chitosan as a wound dressing starting material: antimicrobial properties and mode of action[J].International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2019, 20(23):5899.DOI:10.3390/ijms20235889.
[36] YOUSSEF A M, ABOU-YOUSEF H, EL-SAYED S M, et al.Mechanical and antibacterial properties of novel high performance chitosan/nanocomposite films[J].International Journal Biological Macromolecules, 2015, 76: 25-32.DOI:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2015.02.016.
[37] XING K, CHEN X G, LIU C S, et al.Oleoyl-chitosan nanoparticles inhibits Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus by damaging the cell membrane and putative binding to extracellular or intracellular targets[J].International Journal of Food Microbiology, 2009, 132(2/3):127-133.DOI:10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2009.04.013.
[38] QIN C, LI H R, XIAO Q, et al.Water-solubility of chitosan and its antimicrobial activity[J].Carbohydrate Polymers, 2006, 63(3): 367-374.DOI:10.1016/j.carbpol.2005.09.023.
[39] WANG J, XIA L L, LIU H, et al.Colorimetric microneedle sensor using deep learning algorithm for meat freshness monitoring[J].Chemical Engineering Journal, 2024, 481: 148474.DOI:10.1016/j.cej.2023.148474.
[40] 类红梅, 罗欣, 毛衍伟, 等.天然抗氧化剂的功能及其在肉与肉制品中的应用研究进展[J].食品科学, 2020, 41(21): 267-277.DOI:10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20191025-286.
[41] BORDIGNON J C S, BADARO A T, BARBIN D F, et al.Oxidation of whey protein isolate after thermal convection and microwave heating and freeze-drying: correlation among physicochemical and NIR spectroscopy analyses[J].Heliyon, 2023, 9(7): e17981.DOI:10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e17981.
[42] MOHAN A, ROY A, DUGGIRALA K, et al.Oxidative reactions of 4-oxo-2-nonenal in meat and meat products[J].LWT-Food Science and Technology, 2022, 165: 113747.DOI:10.1016/j.lwt.2022.113747.
[43] ANRAKU M, FUJII T, FURUTANI N, et al.Antioxidant effects of a dietary supplement: reduction of indices of oxidative stress in normal subjects by water-soluble chitosan[J].Food and Chemical Toxicology,2009, 47(1): 104-109.DOI:10.1016/j.fct.2008.10.015.
[44] HERAS M, HUANG C C, CHANG C W, et al.Trends in chitosanbased films and coatings: a systematic review of the incorporated biopreservatives, biological properties, and nanotechnology applications in meat preservation[J].Food Packaging and Shelf Life,2024, 42: 101259.DOI:10.1016/j.fpsl.2024.101259.
[45] ZHAO Y H, ZHANG Y L, DONG H, et al.Functional biopolymers for food packaging: formation mechanism and performance improvement of chitosan-based composites[J].Food Bioscience, 2023, 54: 102927.DOI:10.1016/j.fbio.2023.102927.
[46] YU H Y, GE Y, DING H Q, et al.Vanillin cross-linked chitosan/gelatin bio-polymer film with antioxidant, water resistance and ultraviolet-proof properties[J].International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2023, 253: 126726.DOI:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.126726.
[47] BEIGZADEH GHELEJLU S, ESMAIILI M, ALMASI H.Characterization of chitosan-nanoclay bionanocomposite active films containing milk thistle extract[J].International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2016, 86: 613-621.DOI:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2016.02.012.
[48] LOTFY T M R, SHAWIR S M S, BADAWY M E I.The impacts of chitosan-essential oil nanoemulsions on the microbial diversity and chemical composition of refrigerated minced meat[J].International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2023, 239: 124237.DOI:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.124237.
[49] 赵思琪, 张浪, 刘骞, 等.天然抗菌剂纳米乳液的制备、抑菌机理及在肉类保鲜中的应用研究进展[J].肉类研究, 2022, 36(4): 48-56.DOI:10.7506/rlyj1001-8123-20220117-00.
[50] ZHANG Hv Y, LIANG Y, LI X L, et al.Effect of chitosan-gelatin coating containing nano-encapsulated tarragon essential oil on the preservation of pork slices[J].Meat Science, 2020, 166: 108137.DOI:10.1016/j.meatsci.2020.108137.
[51] SUN Y A, ZHANG M, BHANDARI B, et al.Nanoemulsion-based edible coatings loaded with fennel essential oil/cinnamaldehyde:characterization, antimicrobial property and advantages in pork meat patties application[J].Food Control, 2021, 127: 108151.DOI:10.1016/j.foodcont.2021.108151.
[52] WANG L, LIU T, LIU L, et al.Impacts of chitosan nanoemulsions with thymol or thyme essential oil on volatile compounds and microbial diversity of refrigerated pork meat[J].Meat Science, 2022,185: 108706.DOI:10.1016/j.meatsci.2021.108706.
[53] SONG X Y, WANG L, LIU T, et al.Mandarin (Citrus reticulata L.)essential oil incorporated into chitosan nanoparticles: characterization,anti-biofilm properties and application in pork preservation[J].International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2021, 185: 620-628.DOI:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.06.195.
[54] QIU L Q, ZHANG M, CHITRAKAR B, et al.Effects of nanoemulsion-based chicken bone gelatin-chitosan coatings with cinnamon essential oil and rosemary extract on the storage quality of ready-to-eat chicken patties[J].Food Packaging and Shelf Life, 2022,34: 100933.DOI:10.1016/j.fpsl.2022.100933.
[55] HUANG M S, ZHANG M, BHANDARI B.Recent development in the application of alternative sterilization technologies to prepared dishes: a review[J].Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition,2018, 59(7): 1188-1196.DOI:10.1080/10408398.2017.1421140.
[56] SONI A, SMITH J, THOMPSON A, et al.Microwave-induced thermal sterilization-a review on history, technical progress, advantages and challenges as compared to the conventional methods[J].Trends in Food Science and Technology, 2020, 97: 433-442.DOI:10.1016/j.tifs.2020.01.030.
[57] HASSANZADEH P, TAJIK H, ROHANI S M R, et al.Effect of functional chitosan coating and gamma irradiation on the shelflife of chicken meat during refrigerated storage[J].Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 2017, 141: 103-109.DOI:10.1016/j.radphyschem.2017.06.014.
[58] FANG Z X, LIN D, WARNER R D, et al.Effect of gallic acid/chitosan coating on fresh pork quality in modified atmosphere packaging[J].Food Chemistry, 2018, 260: 90-96.DOI:10.1016/j.foodchem.2018.04.005.
[59] LIU W L, KANG S, XUE J, et al.Self-assembled carboxymethyl chitosan/zinc alginate composite film with excellent water resistant and antimicrobial properties for chilled meat preservation[J].International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2023, 247:125752.DOI:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.125752.
[60] ZENG Z, YANG Y J, TU Q, et al.Preparation and characterization of carboxymethyl chitosan/pullulan composite film incorporated with eugenol and its application in the preservation of chilled meat[J].Meat Science, 2023, 198: 109085.DOI:10.1016/j.meatsci.2022.109085.
[61] ZHAO R N, GUO H C, YAN T Y, et al.Fabrication of multifunctional materials based on chitosan/gelatin incorporating curcumin-clove oil emulsion for meat freshness monitoring and shelf-life extension[J].International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2022, 223: 837-850.DOI:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2022.10.271.